YesWorkflow
YesWorkflow is a modeling and provenance management tool for scripting languages.
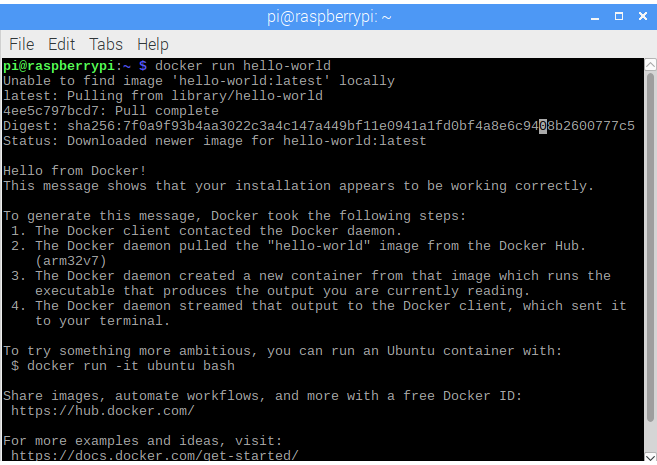
Run Docker image of YesWorkflow
- Download YesWorkflow repository from: https://github.com/yesworkflow-org/yw-docker
- Open a terminal in
yw-clidirectory. - Create a folder named
codesinside current directory. Create a file
example.pywith the following content in thecodesdirectory:import netCDF4 import numpy as np from netCDF4 import ma import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.backends.backend_pdf import PdfPages # @BEGIN main # @PARAM db_pth # @PARAM fmodel # @IN input_mask_file @URI file:{db_pth}/land_water_mask/LandWaterMask_Global_CRUNCEP.nc # @IN input_data_file @URI file:{db_pth}/NEE_first_year.nc # @OUT result_NEE_pdf @URI file:result_NEE.pdf def main(db_pth = '.', fmodel = 'clm'): # @BEGIN fetch_mask # @PARAM db_pth # @IN g @AS input_mask_file @URI file:{db_pth}/land_water_mask/LandWaterMask_Global_CRUNCEP.nc # @OUT mask @AS land_water_mask g = netCDF4.Dataset(db_pth+'/land_water_mask/LandWaterMask_Global_CRUNCEP.nc', 'r') mask = g.variables['land_water_mask'] mask = mask[:].swapaxes(0,1) # @END fetch_mask # @BEGIN load_data # @PARAM db_pth # @IN input_data_file @URI file:{db_pth}/NEE_first_year.nc # @OUT data @AS NEE_data f = netCDF4.Dataset(db_pth+'/NEE_first_year.nc', 'r') data = f.variables['NEE'] data = data[:] data = data.swapaxes(0,2) adj = 60*60*24*(365/12)*1000 data = data*adj # @END load_data # @BEGIN standardize_with_mask # @IN data @AS NEE_data # @IN mask @AS land_water_mask # @OUT data @AS standardized_NEE_data native = data.mean(2) latShape = mask.shape[0] logShape = mask.shape[1] for x in range(latShape): for y in range(logShape): if mask[x,y] == 1 and ma.getmask(native[x,y]) == 1: for index in range(data.shape[2]): data[x,y,index] = 0 # @END standardize_with_mask # @BEGIN simple_diagnose # @PARAM fmodel # @IN data @AS standardized_NEE_data # @OUT pp @AS result_NEE_pdf @URI file:result_NEE.pdf plt.imshow(np.mean(data,2)) plt.xlabel("Mean 1982-2010 NEE [gC/m2/mon]") plt.title(fmodel + ":BG1") pp = PdfPages('result_NEE.pdf') pp.savefig() pp.close() # @END simple_diagnose # @END mainCurrent directory structure:
. ├── build.sh ├── codes │ └── example.py ├── Dockerfile ├── run.ps1 └── run.shBuild Docker image based on the
Dockerfile:docker build -t yesworkflow .Run Docker image by mounting the
codesdirectory as volume:docker run --rm -it -v $(pwd)/codes:/codes yesworkflowThis will open a session in YesWorkflow environment:
yw@be484cd73b89:~$ pwd /home/ywChange directory to the
codesdirectory in YesWorkflow session:cd /codesCreating a workflow graph for a script: We will use the
graphcommand to produce a graphical representations of the script based on the YW comments it contains. Run the example python program:yw graph example.pyIt will output the result to the terminal.
Storing output to file: YesWorkflow natively outputs GraphViz’s DOT format (file extension
.gv). We can store the output to a fileexample.gv:yw graph example.py>example.gvGenerating Graph PDF: Render DOT output file (
example.gv) as PDF file using Graphviz’s dot command:dot -Tpdf example.gv -o example.pdfCheck the
\codesfolder and it will contain the graph pdf fileexample.pdf.Directory structure after creating the DOT file and PDF file:
. ├── build.sh ├── codes │ ├── example.gv │ ├── example.pdf │ └── example.py ├── Dockerfile ├── run.ps1 └── run.sh
Exit YesWorkflow session: To exit the session press
ctrl+d.The output PDF
example.pdf: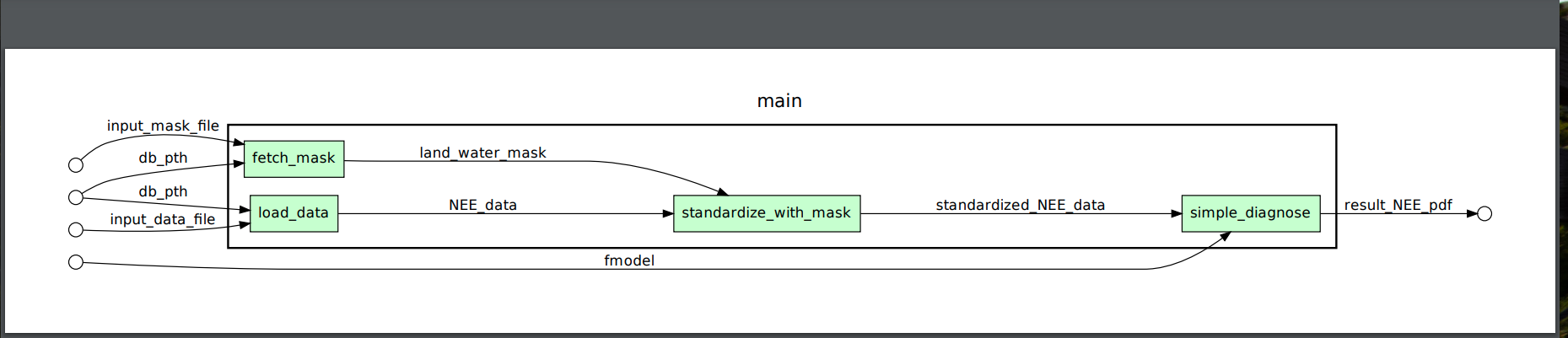
Reference
Advertisement