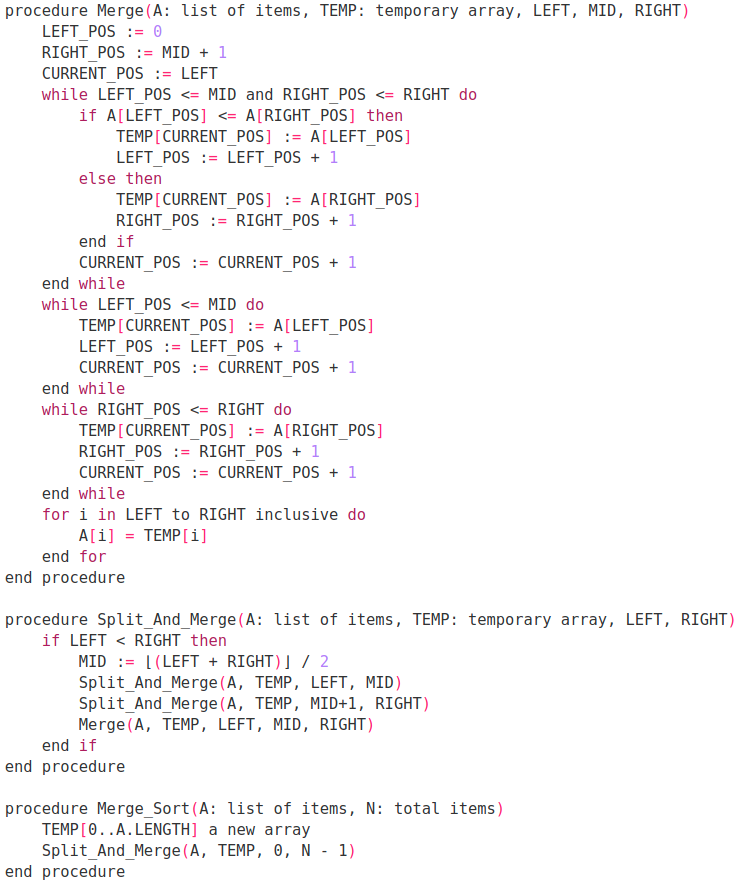
Sorting Algorithm Comparisons Table
| Criteria | Bubble | Selection | Insertion | Merge | Quick | Counting | Timsort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | Brute force | Brute force | Brute force | Divide-and-conquer | Divide-and-conquer | Non comparison | Hybrid |
| Worst Time | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(nlgn) | O(n2) | O(k+n) | O(nlgn) |
| Average Time | Θ(n2) | Θ(n2) | Θ(n2) | Θ(nlgn) | Θ(nlgn) | Θ(k+n) | Θ(nlgn) |
| Best Time | Ω(n) | Ω(n2) | Ω(n) | Ω(nlgn) | Ω(nlgn) | Ω(k+n) | Ω(n) |
| Space | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(k+n) | O(n) |
| Stable | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| In-place | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| Online | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Adaptive | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Suitable for | Sorted list | Almost sorted list | List with unknown order | 0<=A[i]<=k |
Criteria Explanation
- Technique: Methodology of the sorting algorithm.
- Worst Time: Worst time complexity (Big-O) of the algorithm.
- Average Time: Average time complexity (Big-Theta) of the algorithm.
- Best Time: Best time complexity (Big-Omega) of the algorithm.
- Space: Space complexity of the algorithm.
- Stable: Stable algorithm maintains the relative order of input elements with equal values.
- In-place: In-place algorithm does not use auxiliary data structure to transform the input elements.
- Online: Online algorithm does not require the entire input available from the start.
- Adaptive: Adaptive algorithm takes the advantages of presorted array elements.
Reference
- Introduction to algorithms by Cormen, Thomas H and Leiserson, Charles E and Rivest, Ronald L and Stein, Clifford
- Bubble sort
- Insertion sort
- Merge sort
- Counting sort
- Sorting Algorithm - Wikipedia
- Timsort - Wikipedia
- Timsort - C2 article
- Analysis of different sorting techniques - Geeksforgeeks
Advertisement