Manually cropping and merging a large number of images can be a boring and time-consuming task. We can automate this boring stuff with Python and the OpenCV library1. In this tutorial, we’ll explore how to crop and merge multiple images using Python and OpenCV.
Scenario
Suppose we have a collection of similar images, and we want to crop them at a certain location before merging every two images together.
The images are 600px X 600px in size, and there’s a fixed region where we want to perform the cropping.
For example, let’s consider the following two brain image figures:
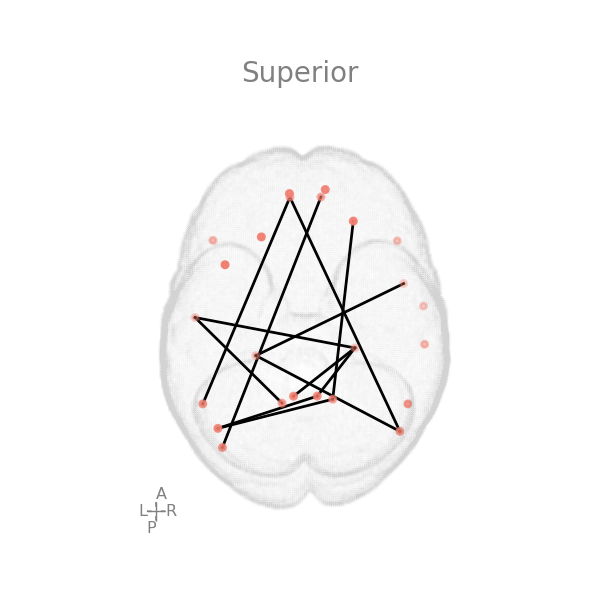 First image: this will be placed on left side
First image: this will be placed on left side
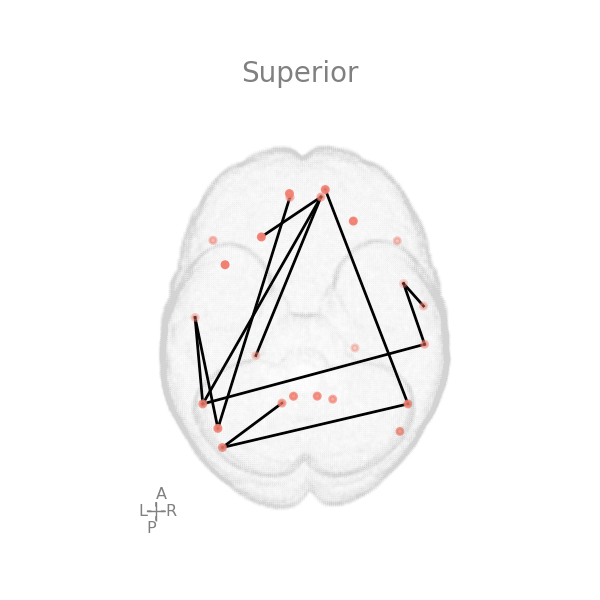 Second image: this will be placed on right side
Second image: this will be placed on right side
Our goal is to crop the outer white spaces and the text on top, and then merge the two images into a single image like the following:
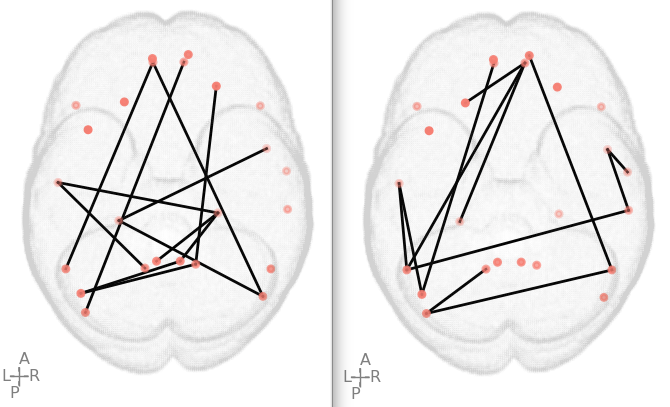 Manually merged image: this image is manually merged from the above two images
Manually merged image: this image is manually merged from the above two images
Automate the cropping and merging of images using Python
Step 1: Determine the coordinates in the images for cropping
To crop an image using code, we need to know the exact pixel location and size of the region to crop. In this case, we’ll use an online tool to get the coordinates where we need to crop 2.
The top-left corner of the image is represented by the coordinate (0, 0).
In our example, the desired position to start cropping is (130, 140), with a size of 350px X 400px.
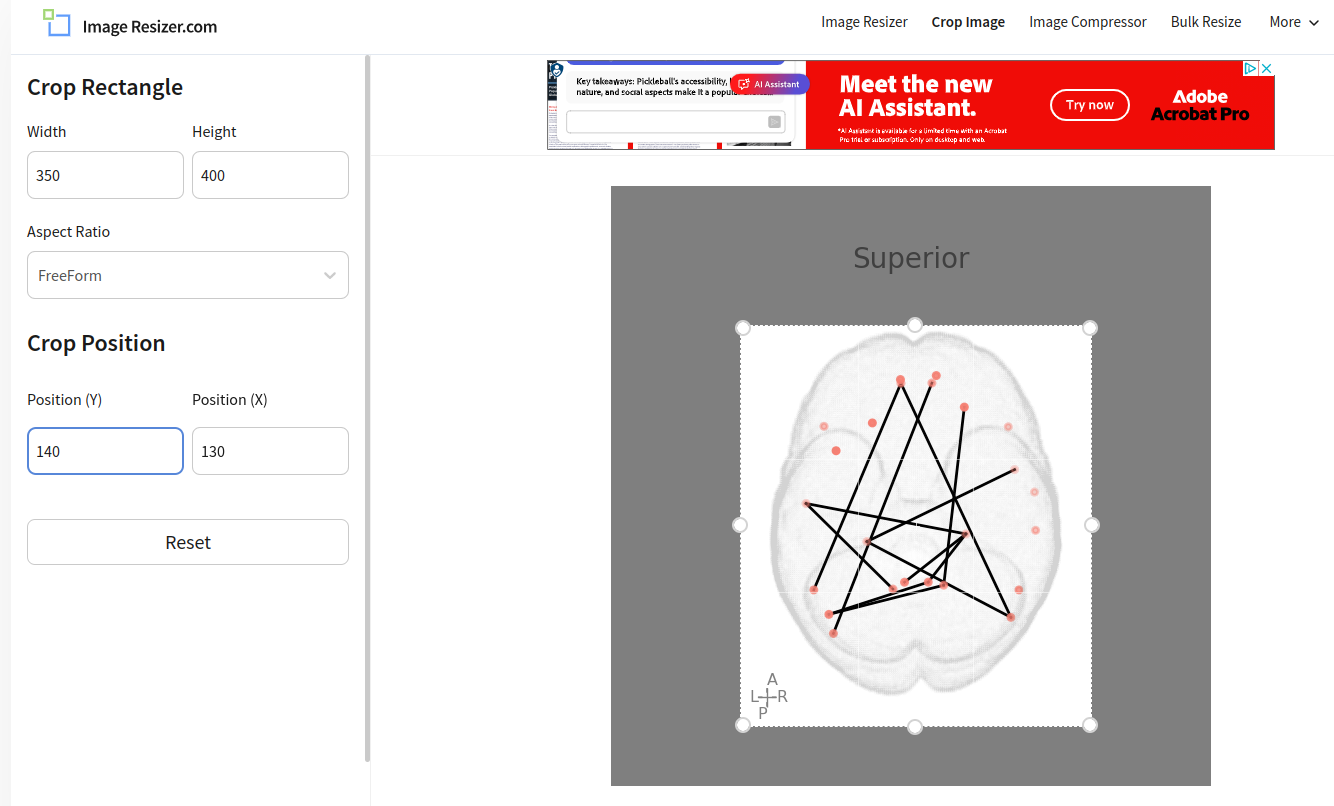 Calculating the start coordinates and desired image size using an online crop tool
Calculating the start coordinates and desired image size using an online crop tool
Step 2: Use Python to crop and merge the images
- First, we need to install the
opencv-pythonpackage, which will be used to crop and merge the images:
pip install opencv-python
- The following code will read the images, crop the specified regions, merge them side by side, and save the result as a new image file.
import cv2
def crop_and_merge():
combined_image_file = "paper_exp/survey_1/1.png"
left_image_file = "paper_exp/survey_1/1_r_1_645_mid.png"
right_image_file = "paper_exp/survey_1/1_r_1_2500_mid.png"
# Load the images
left_image = cv2.imread(left_image_file)
right_image = cv2.imread(right_image_file)
# Set the crop parameters
x_start = 130
y_start = 140
crop_width = 350
crop_height = 400
# Crop the images
cropped_left_image = left_image[y_start:y_start + crop_height, x_start:x_start + crop_width]
cropped_right_image = right_image[y_start:y_start + crop_height, x_start:x_start + crop_width]
# Combine the images horizontally (side by side)
combined_image = cv2.hconcat([cropped_left_image, cropped_right_image])
# Save the combined image
cv2.imwrite(combined_image_file, combined_image)
print(f"Saved: {combined_image_file}")
# Call the function to crop and merge the images
crop_and_merge()
In this code:
- We first load the left and right images using
cv2.imread(). - We set the crop parameters
(x_start, y_start, crop_width, and crop_height)based on the coordinates obtained in Step 1. - We crop the images using array slicing.
- We combine the cropped images horizontally using
cv2.hconcat(). - Finally, we save the combined image using
cv2.imwrite().
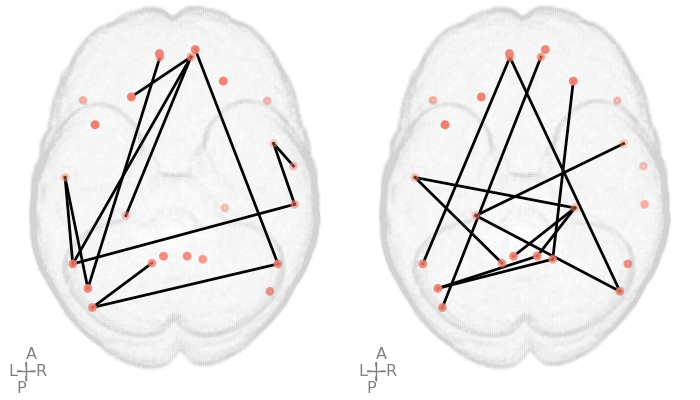 Automatically cropped and merged image: This image is automatically created from the above two images
Automatically cropped and merged image: This image is automatically created from the above two images
By automating the process of cropping and merging images with Python and OpenCV, we can save a significant amount of time and effort, especially when dealing with a large number of images.
References:
Advertisement